
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping Human Resources by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving employee engagement. From recruitment to performance evaluations, AI for HR offers transformative benefits, such as increased efficiency and data-driven insights. However, integrating AI in HR raises significant ethical and legal challenges, including bias, transparency, data privacy, and job security. Addressing these concerns is crucial for organizations to maintain trust and fairness.
This article explores the foundational ethics and challenges of AI for HR.
AI in HR is revolutionizing how organizations manage their workforce. By leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing, AI streamlines processes and enhances strategic decision-making. According to Personnel Today, 38% of organizations already use AI for HR, with 62% planning to adopt it within three years.
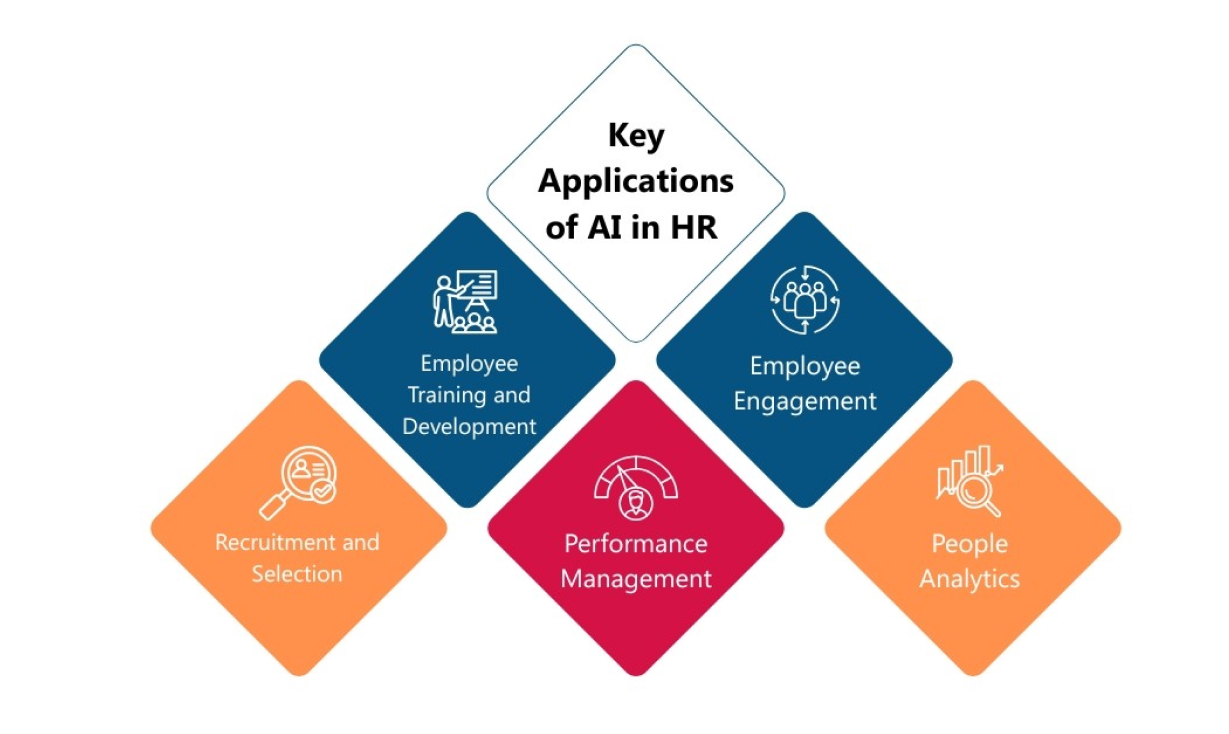
Despite these advantages, the ethical implications of AI in HR demand careful consideration to ensure responsible deployment.
The integration of AI for HR introduces complex AI ethics challenges that impact fairness, trust, and employee rights. Addressing these issues is essential for maintaining an equitable workplace.
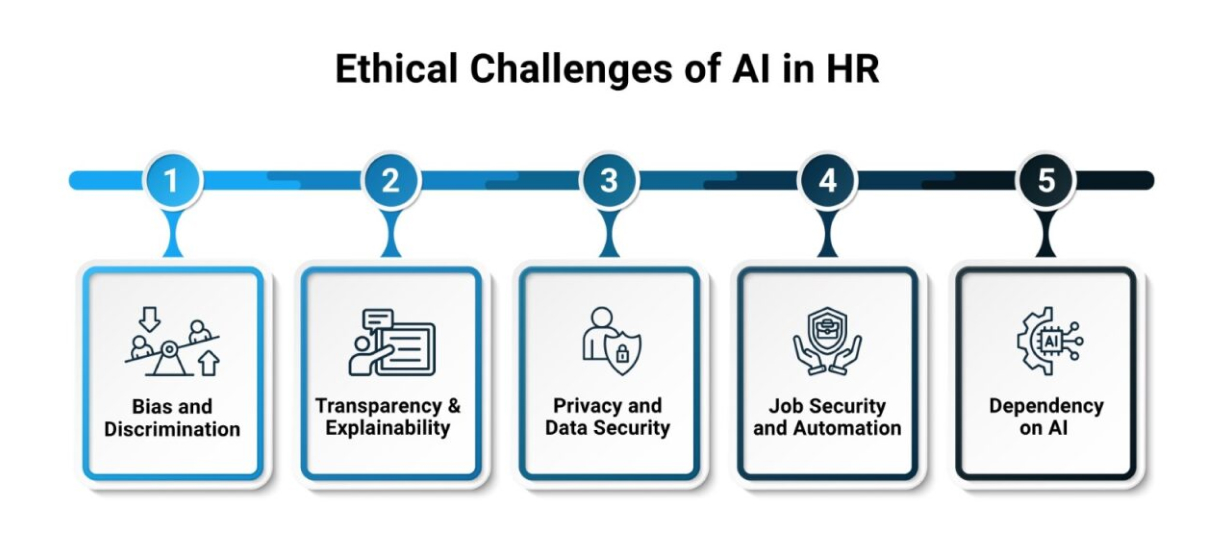
AI systems can perpetuate biases present in training data, leading to unfair outcomes in hiring, promotions, or evaluations. For instance, Amazon’s AI recruiting tool, scrapped in 2018, favored male candidates because it was trained on male-dominated resumes, penalizing terms like “women’s.”
Mitigation Strategies
Opaque AI decisions can erode employee trust. For example, employees may not understand why an AI system assigned a low performance score, leading to dissatisfaction. AI ethics emphasizes explainable systems to foster accountability.
Mitigation Strategies
AI in HR relies on sensitive employee data, raising privacy concerns. Mishandling data, such as emails or performance metrics, can lead to breaches, with 1,108 reported in 2020 alone. Compliance with regulations like GDPR is critical.
Mitigation Strategies
AI-driven automation can displace jobs, causing employee anxiety. For example, Uber’s AI performance monitoring system was criticized for excessive surveillance, increasing driver stress. Organizations must balance efficiency with employee welfare.
Mitigation Strategies
Over-reliance on AI risks diminishing human judgment in nuanced HR decisions. For instance, fully autonomous systems may overlook contextual factors in performance evaluations.
Mitigation Strategies
Deploying AI for HR involves navigating legal frameworks to avoid liabilities and ensure compliance.
Compliance with laws like GDPR is essential when handling employee data. GDPR mandates explicit consent, transparent processing, and robust security measures. Non-compliance can lead to significant fines.
Compliance Strategies
AI systems must avoid discriminatory practices based on race, gender, or age. Biased algorithms can violate equal employment laws, leading to lawsuits and reputational damage.
Compliance Strategies
AI applications, such as performance monitoring, must respect employee privacy and fair labor practices. Excessive surveillance can create hostile work environments, violating labor laws.
Compliance Strategies
Organizations must ensure AI systems operate within legal boundaries. Regular audits and clear policies mitigate risks of non-compliance.
Compliance Strategies
From streamlining hiring processes to improving candidate experiences, companies like Unilever and Hilton showcase how ethical AI can enhance efficiency and inclusivity. These case studies highlight both the promise and pitfalls of using AI in HR—and why responsible implementation is key.
Unilever’s success demonstrates the benefits of ethical AI design, while Amazon’s failure underscores the risks of unchecked biases. These cases highlight the need for transparency, fairness, and compliance in AI for HR.
To address AI ethics challenges, HR leaders should adopt the following best practices:
The future of AI in HR will be defined by stronger ethical frameworks, evolving regulations, and a proactive approach to workforce impact. HR professionals must rise to the challenge—combining data-driven insights with a renewed commitment to fairness and accountability.
Developing comprehensive AI ethics frameworks is essential for guiding responsible AI in HR. These frameworks should address fairness, transparency, and accountability, adapting to technological advancements. Ongoing research into bias mitigation and explainability will refine these guidelines.
Staying informed about evolving regulations, such as GDPR and anti-discrimination laws, is crucial. Organizations should collaborate with legal experts to anticipate changes and ensure compliance.
Long-term studies on AI’s impact on job satisfaction and organizational culture will provide insights into balancing automation with human-centric values. Reskilling programs will be key to mitigating job displacement.
HR teams must evolve into strategic partners, leveraging AI insights for data-driven decisions while prioritizing ethics. Training HR staff on AI capabilities will maximize benefits and ensure responsible use.
AI for HR offers transformative potential, streamlining recruitment, training, performance management, and engagement. However, AI ethics challenges—bias, transparency, privacy, job security, and dependency—require proactive solutions. Legal challenges, including GDPR compliance and anti-discrimination laws, demand rigorous oversight. By adopting best practices like regular audits, transparent processes, human oversight, and robust data protection, organizations can harness AI in HR responsibly.
As AI evolves, HR leaders must prioritize AI ethics, engage stakeholders, and invest in reskilling to create a fair, transparent, and inclusive workplace. By navigating these challenges, AI for HR can enhance strategic decision-making while upholding employee rights and organizational values in 2025 and beyond.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.