
When assessing the performance of employees, a manager primarily focuses on two aspects:
On the basis these parameters, they are likely to find the following categories of employees:
Assessing the performance of employees is essential in planning their career paths and ultimately transitioning them into future, senior roles— otherwise known as succession planning. When performance is properly assessed, it becomes easier to identify and coach those with the potential to become future leaders. This helps to understand the strength of team members with their roles and grooms them for future growth within the firm.
The question, then, is how to find such potential leaders among the performance categories of employees.
The 9-box grid is a talent management tool widely used by managers to evaluate the performance versus potential of employees and to guide their plans for employee development and succession. On the x-axis is performance, measured by performance reviews; on the y-axis is potential, the likelihood of moving up a couple of levels in managerial or professional roles.
The 9-box grid has its roots in the 1970s, when management consulting firm McKinsey created it as an assessment framework to help General Electric (GE) prioritize its investments across business units. It was then known as the GE-McKinsey nine-box framework and it was inspired by the growth-share matrix from the Boston Consulting Group. The structure, though, was a bit different – it plotted industry attractiveness against competitive strength, to guide the investment decision. Since then, HR has adapted the grid to cover recruitment and selection purposes by changing the axial parameters as per their purposes.
Being a key part of the performance management process, the grid requires HR and talent managers to put their heads together and assign employees to relevant boxes on the grid, based on their assessed levels of performance and potential. The conversation must be comprehensive, though the process itself is iterative – insights from assessing one employee could well shift the assessment of the other. Competitor actions or organizational objectives could also alter perspectives on how valuable current aptitude areas will be in the future.
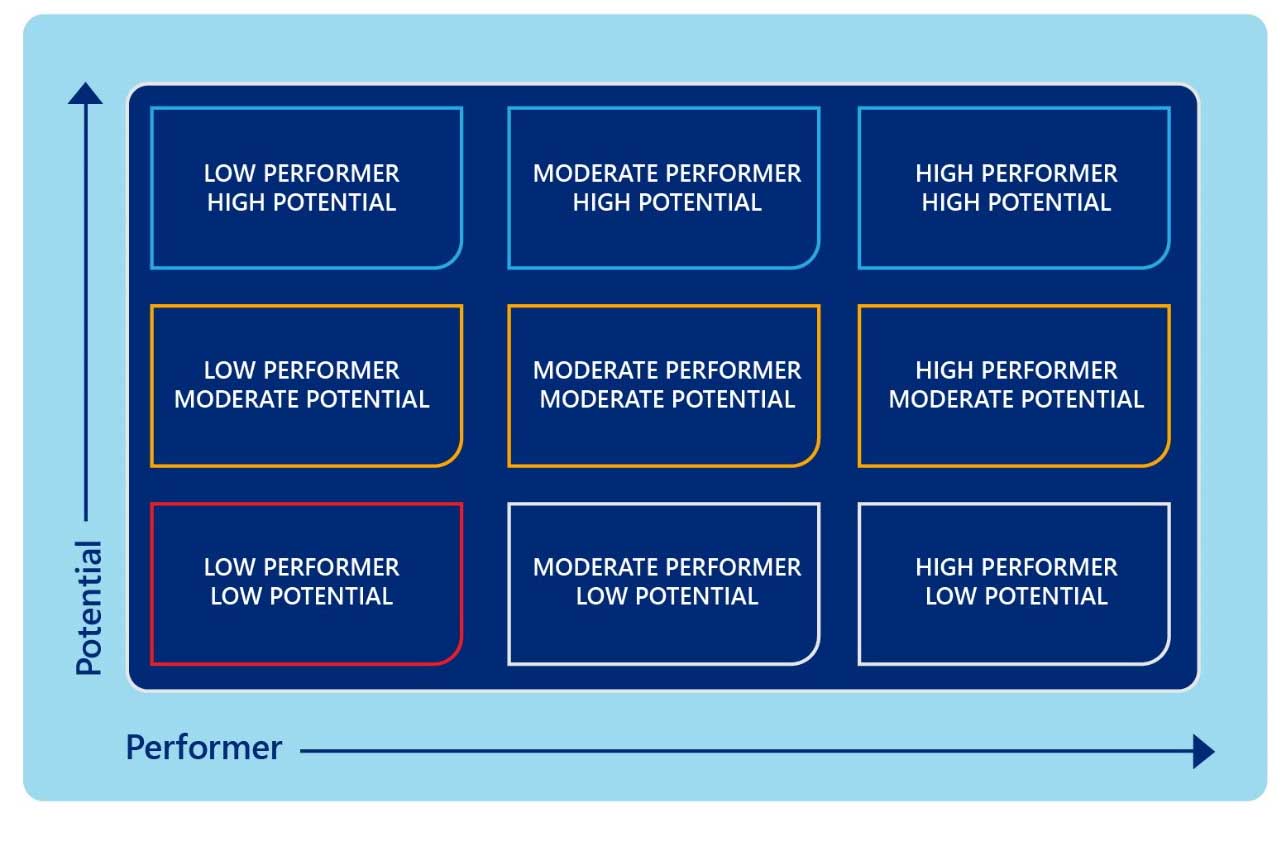
Here is what the 9-box grid looks like:
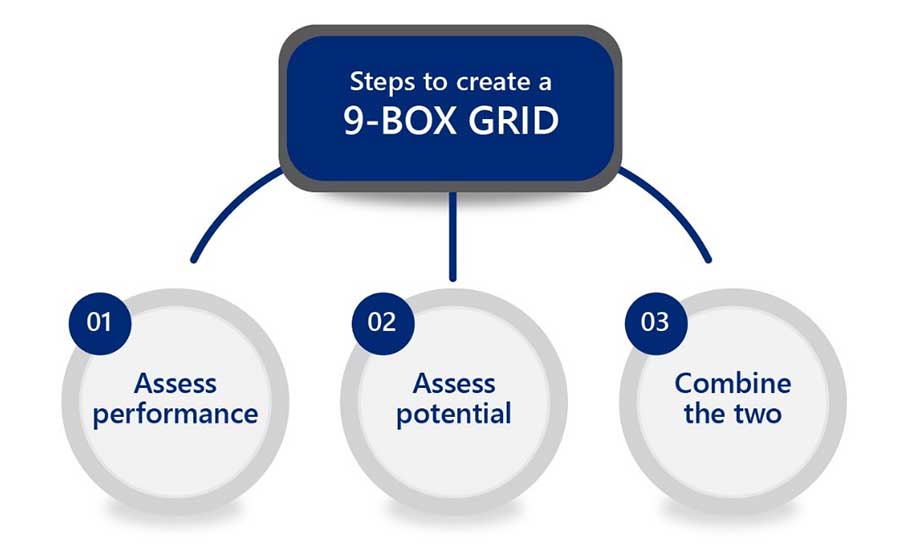
The process requires diligence, and comprises three steps:
What gives the 9-box grid its power is its effectiveness and simplicity. It requires clear, transparent communication but provides excellent results when this is in place and other aspects of the performance review are properly assessed. The most valuable position to be in is the top right – the highest rank in both performance and potential. Conversely, the bottom left – the lowest performance and potential – is the least desirable.
Below are the key attributes of employees placed in each of the nine boxes:
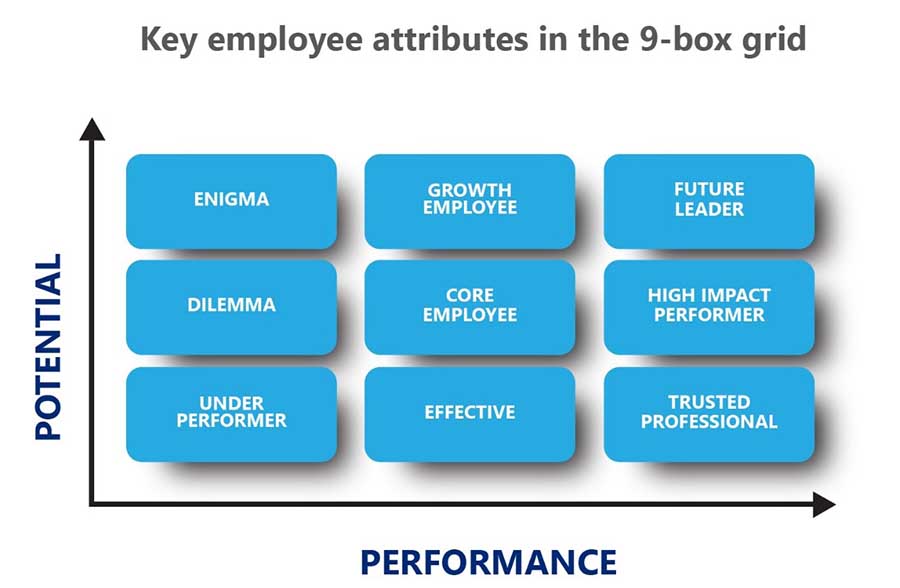
Creating a 9-box grid kicks off much-needed constructive dialogue, further spurring discussion, development, and teamwork. Figuring out where each employee fits in the grid helps in succession planning and understanding where each employee must be in future organizational changes. Those in the upper right have bright prospects for succession; those in the bottom left may need reassignment or may find themselves on their way out.
The idea of the nine boxes is to indicate where HR needs to focus its succession planning efforts through investments in future leaders.
This makes great sense from a strategic perspective and in planning resource allocation. A business would want to invest in employees who provide the largest return and aid in creating the biggest competitive advantage. Investing instead in a bad hire would take away scarce resources from top performers.
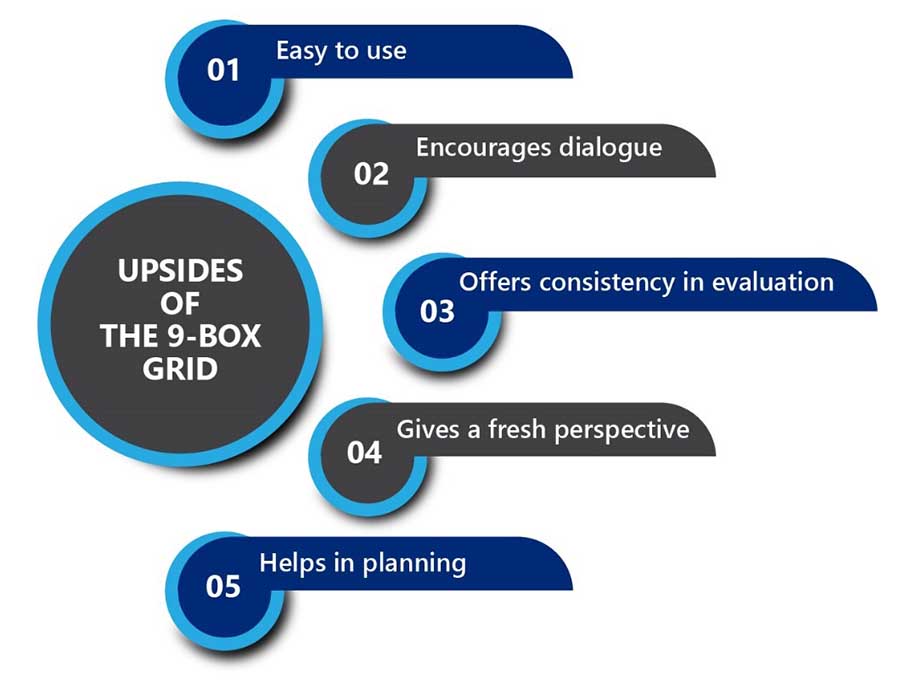
The grid has several benefits to offer when it comes to the recruitment and selection process. The key upsides are:
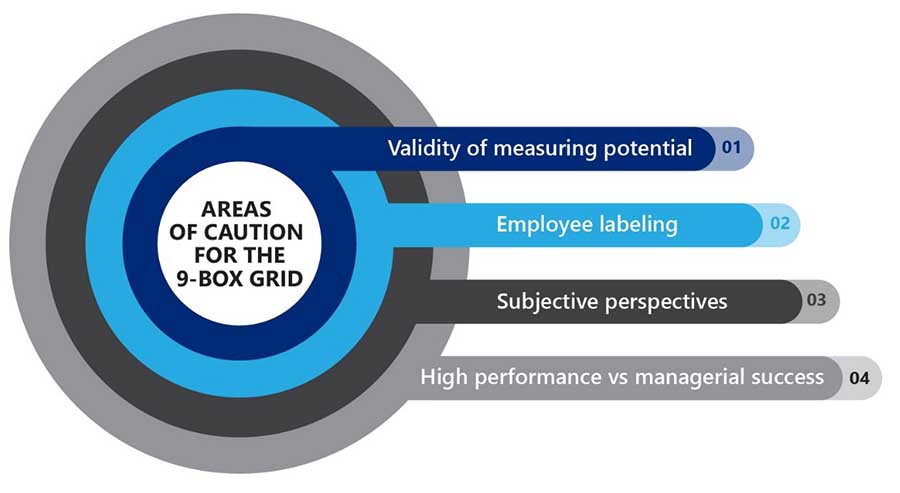
Assessing potential is no easy task, making it difficult to accurately position employees in the grid and execute succession plans accordingly. Here are other areas of caution:
The 9-box grid remains an effective talent management tool to encourage discussion around the performance and potential of the workforce and facilitate the achievement of organizational goals. Clear discussion and definition are essential for the grid to be used fluently. It remains vital to establish the outcomes sought from the exercise before starting it and to act on the discussion so that the grid does not just become an exercise in futility!
Follow TMI for more insights on employee performance and future potential.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.