
An HR scorecard is a strategic measurement tool that assesses and enhances the human resources department's contributions to overall business goals. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to workforce productivity, hiring, retention, and training, the scorecard helps connect HR initiatives to tangible business results.
This enables leadership to make data-backed decisions when investing in HR programs as well as identify areas needing improvement. In short, an HR scorecard brings accountability by making the HR department’s impact quantifiable.
This guide will walk you through the core components of designing and implementing an effective Human Resource scorecard tailored to your organization’s needs.
An HR scorecard is a specialized balanced scorecard focused solely on human capital metrics. It establishes benchmarks and assesses if HR initiatives meet desired outcomes that further organizational strategy.
An HR scorecard stands apart from standard HR reports in two key aspects:
It is Strategy-Focused
An HR scorecard differs from generic HR reports in that it is strategy-focused and aligned with the organization's core business objectives. The key performance indicators (KPIs) tracked in an HR scorecard are specifically chosen based on how they relate to and impact strategic goals. For example, the scorecard could track metrics like:
These KPIs provide insights into the workforce elements that drive strategic success. An HR scorecard highlights the vital few HR metrics that impact finances, operations, customer satisfaction, and other corporate priorities.
On the other hand, generic HR reports tend to lack this sharp strategic focus. They include general statistics on hiring volumes, training hours logged, demographics, and payroll processing times. While informative, these generic metrics don't clearly tie to business goals and could even dilute the impact of the scorecard.
An HR scorecard also sets specific targets based on strategic needs and benchmarks. For instance, the organization might set a target revenue per employee of $325,000. Generic reports just present numbers without such context around organizational needs. This strategic alignment of HR KPIs, relevant targets, and tie-ins to corporate objectives is the hallmark of a value-adding HR scorecard.
It Drives Action
The second major difference is that an HR scorecard goes beyond passive reporting to actively drive change. The strategic metrics and preset targets prompt action when shortfalls occur. If revenue per employee drops below $325,000, for example, the HR team dives deeper into the possible root causes—lack of training, low engagement scores, missing skills, etc. Generic reports, on the other hand, simply present the numbers without sparking action or accountability.
Additionally, an effective HR scorecard should clearly map each metric to a "metric owner" - a business leader or HR manager responsible for improving that particular KPI. So if the cost per hire rises, the recruiter is expected to investigate and remedy the situation with due support from business heads in talent acquisition planning and budgeting.
This single-point accountability ensures the HR scorecard does more than just inform. It sets change in motion by making specific leaders responsible for reaching defined targets. The leaders address gaps revealed by the data through improvements in HR programs, processes, tools, and interventions. Over time, an action-oriented scorecard significantly transforms workforce capability and directly elevates performance on corporate strategic goals.
In short, an HR scorecard enables data-backed business decisions about HR functions. It empowers the department to operate as a strategic asset rather than just an administrative function.
Follow these best practices when developing your HR scorecard:
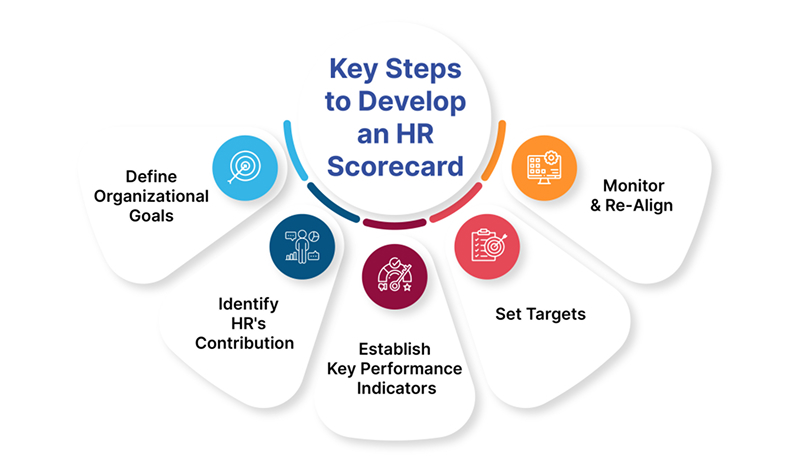
1. Define Organizational Goals
The first step in developing an HR scorecard is to clearly define the top 3-5 organizational goals for the year. These are the high-level objectives that the business wants to achieve in areas like:
These organizational goals reflect business priorities and strategy. The HR scorecard will eventually connect HR initiatives back to moving the needle on these metrics.
2. Identify HR's Contribution
After defining the 3-5 top organizational goals, the next step is determining HR's role in achieving each target. Analyze how HR activities, programs, and systems influence or drive performance for that business objective.
For example:
The idea is to zone in on the specific HR focus areas that have the highest correlation and influence over those organizational goals.
3. Establish Key Performance Indicators
With the HR focus areas identified, now outline 3-5 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) under each organizational goal that quantify the impact of HR efforts.
These KPIs should be:
For example, for the revenue growth goal, KPIs would include:
The KPIs serve as yardsticks for progress against each organizational goal.
4. Set Targets
The next step is establishing performance targets for each KPI that state the measurable outcome HR initiatives aim to drive over a set timeframe (e.g. the next year). The targets should act as goalposts for the HR department.
When setting targets, build in:
For example, a sample target could be to increase annual sales per employee from $110,000 to $130,000 by year-end through a focused hiring and onboarding program.
5. Monitor & Re-Align
The final step is consistent monitoring against the KPI targets through balanced review cycles - either quarterly or biannually. If any metrics fail to show adequate progress, investigate why and realign programs appropriately.
For example, if sales per employee stays flat despite new hiring initiatives, probe deeper into onboarding practices. Use insights to refine strategy and activities. This closes the loop to ensure HR efforts continue influencing organizational goals.
By following these five steps, you can build an HR scorecard tailored to your organization’s unique strategy and needs.
To simplify the process, you can use this pre-built HR Scorecard Template. It lets you outline organizational goals, link relevant HR focus areas, assign metrics and KPIs, and track progress over time.
1. HR Scorecard Template Preview
This visually engaging template makes it easy to communicate HR's impact and get leadership buy-in on talent programs. You can easily customize it further using built-in Excel features.
2. Key HR Metrics to Track
The specific KPIs to include depend entirely on your organization's strategy and priorities. However, some typical HR metrics to consider are:
HR scorecards often break down these metrics further by department, location, or employee segments to spot areas of variance.
By reflecting strategic goals more granularly, you gain clearer insights on where to refine programs.
3. Getting Leadership Buy-In
The effectiveness of an HR scorecard depends largely on leadership paying attention once created. Get better traction by:
This drives home the message that strategic HR not only impacts but also enables business success.
4. Tracking Progress Over Time
An HR scorecard isn't a one-time project. To be useful, it needs consistent monitoring at set intervals. Baseline where your numbers stand today. Then review on a quarterly or half-yearly basis to track trends over time.
Periodic analysis brings out patterns – Do some metrics see linear progress while others stagnate? Does one location or department skew results across the organization? What initiatives appear to move the needle most significantly on strategic KPIs?
These findings help continuously refine programs, processes, and interventions to improve HR contributions. It also makes the business case for HR investment stronger each year.
Over time, your HR scorecard provides an indexed view of the function’s evolution. It cements HR's identity as a value creator, not just a cost center.
An HR scorecard is a powerful tool to demonstrate tangible ROI from people investments, boost talent program effectiveness, and reveal process gaps. It enables data-backed decisions to refine initiatives over time. By starting off on the right foot – with an aligned strategy, ownership and effective design principles – you can build an HR scorecard that sustains as a catalyst for long-term success.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.