
Human resources play a pivotal role in the success of any organization. With evolving business landscapes, it becomes imperative for companies to develop robust human resource management (HRM) practices that align with their business goals. This is where the Human Resources Management Model of Warwick comes into the picture.
The Warwick Model of HRM is an influential framework that examines the relationship between HRM policies and practices with organizational performance and outcomes. It was proposed by two researchers - Hendry and Pettigrew from the University of Warwick in the 1990s.
Over the years, this model has helped HR professionals and business leaders create people-centric policies keeping the larger business objectives in mind. This article will explore what exactly the Warwick Model encompasses, its core components, and its main advantages and disadvantages for modern-day HRM.
The Warwick Model of HRM is a strategic framework used to identify, evaluate and manage different internal and external factors that impact human resource management in an organization.
It examines the interplay between outer context or macro-environmental forces and inner organizational context to create HRM strategies focused on improving performance and organizational effectiveness.
The model emphasizes that HR strategies need to consider both the internal workforce and external landscape to drive strategic outcomes. The inner workings of an HR department should be integrated well with the core business strategy.
As discussed earlier, the Warwick Model has five integral components that come together to create effective HRM policies and practices. Let us look at these components closely:
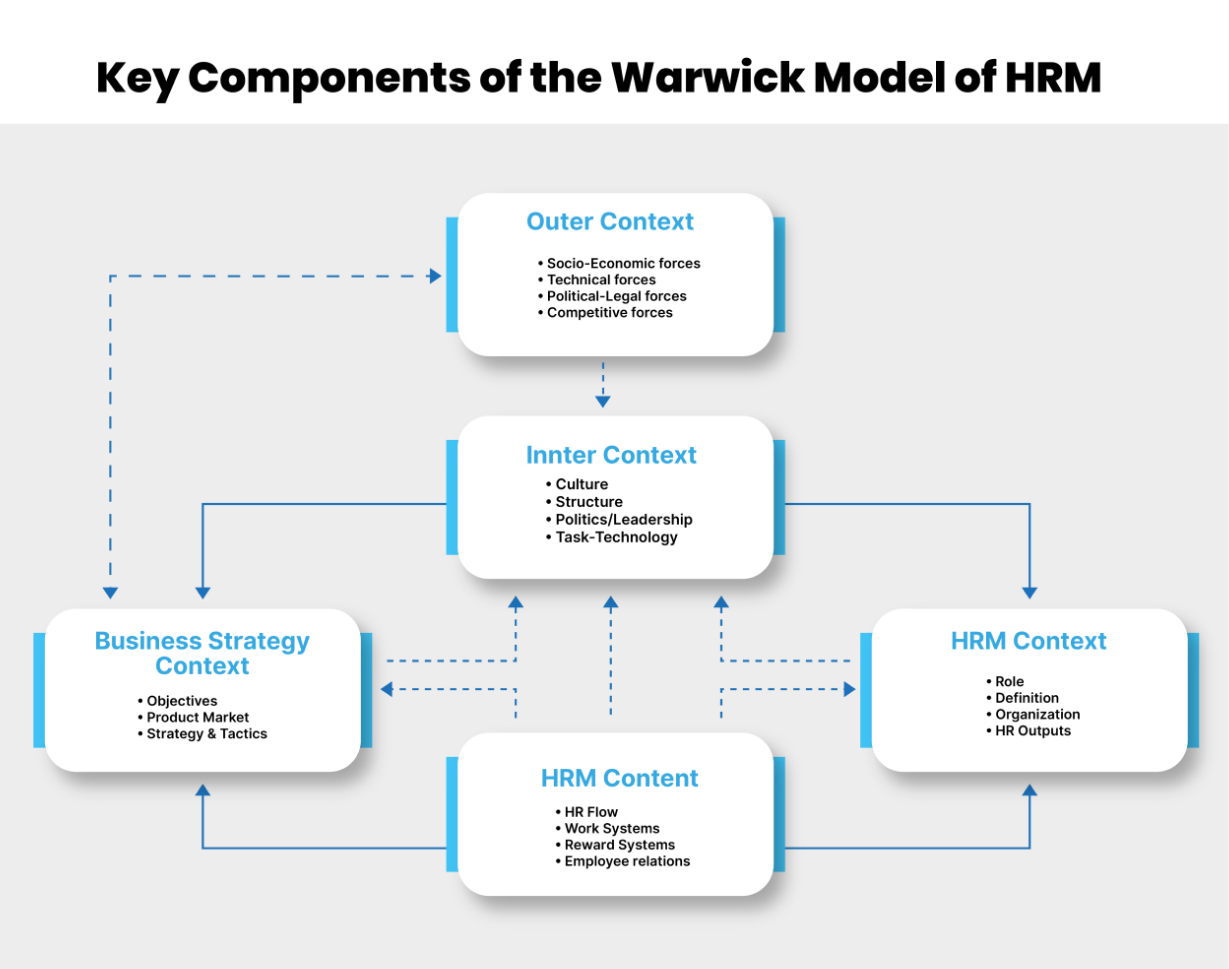
The outer context refers to the external macro-environmental forces that influence an organization's HRM policies and practices. It includes factors such as:
The inner context refers to the internal, organizational forces that shape HRM strategy. It includes:
This refers to the business objectives, competitive positioning and priorities that should inform and align with the HR strategy around:
This focuses on how the HR department itself is structured, positioned and empowered through:
Finally, the HRM content covers the actual interventions and programs to manage people including:
Some benefits of adopting the Warwick Model are:
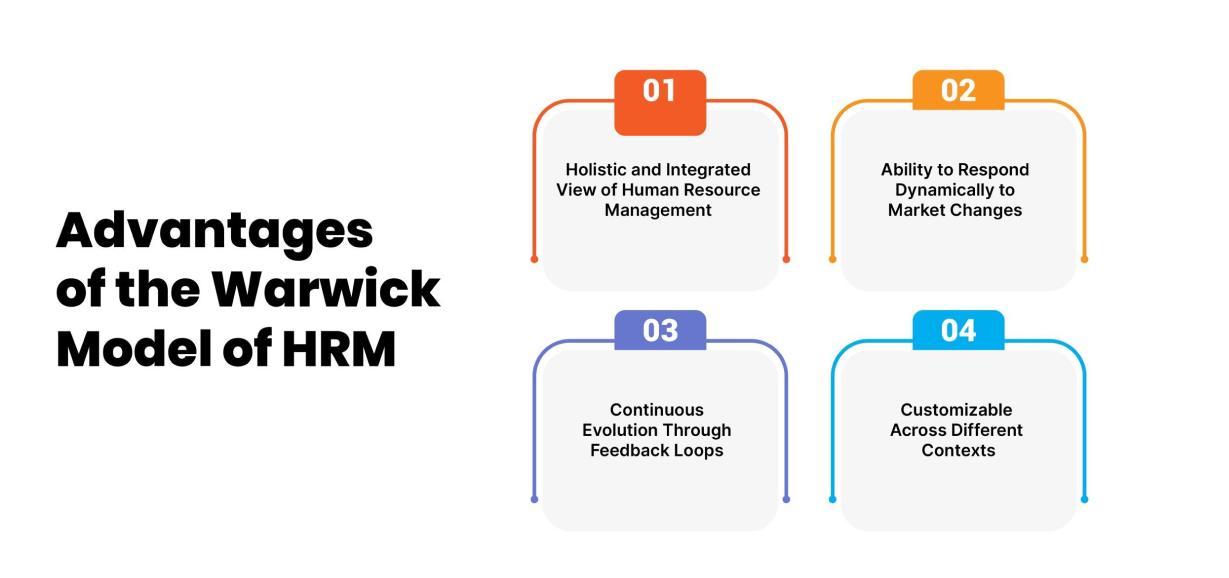
One of the biggest advantages of the Warwick Model is that it offers a holistic and integrated view of managing human resources. Instead of looking at HR initiatives in silos, this model aligns human resource management to the overall business strategy and objectives. This ensures that investments made in the HR function generate optimal returns by improving organizational performance and productivity.
The integrated approach also leads to better collaboration between the HR department and business leaders. With a common understanding of business goals, the HR function is empowered to make people-related decisions that drive growth.
The Warwick Model clearly maps all internal and external factors that impact human resource management in an organization. This includes the outer context consisting of political, economic, social, technological and legal factors. It also maps the inner organizational context including structure, culture and leadership.
By tracking these contextual factors, HR is in a better position to predict and adapt to market changes in a dynamic manner. Any shifts in the business environment can be quickly responded to by realigning people policies and processes. This agility and flexibility is a key advantage of adopting this model.
The Warwick Model emphasizes objective data-driven decision making while framing workforce policies. HR decisions are made based on evidence regarding outer and inner business contexts, strategy requirements and expected HR outcomes. Relying purely on instincts is avoided.
The data-focused approach also helps showcase the direct impact of human resource management on profitability and other financial metrics. This enables the HR function to quantify its contributions and gain credibility within the organization.
The Warwick Model has inbuilt feedback loops that connect the outer context, organizational strategy, HR policies and eventual HR outcomes. Information flows back and forth between these elements.
For instance, changes in social or technological contexts may require realignment of business strategy, which then requires new HR initiatives, eventually impacting metrics like employee productivity. These feedback flows enable continuous evolution of policies and processes to match external shifts.
While being comprehensive, the Warwick Model is also highly customizable for different types of industries, organizations and employee demographics. For instance, a start-up in the technology sector would focus more on culture, innovation and skill development compared to a traditional manufacturing company. The model can be tailored accordingly.
The broad framework ensures that no major factor is missed out, while also allowing adaptation to meet specific needs. This makes the Warwick model universally applicable for HR management across contexts.
Some limitations of this model are:
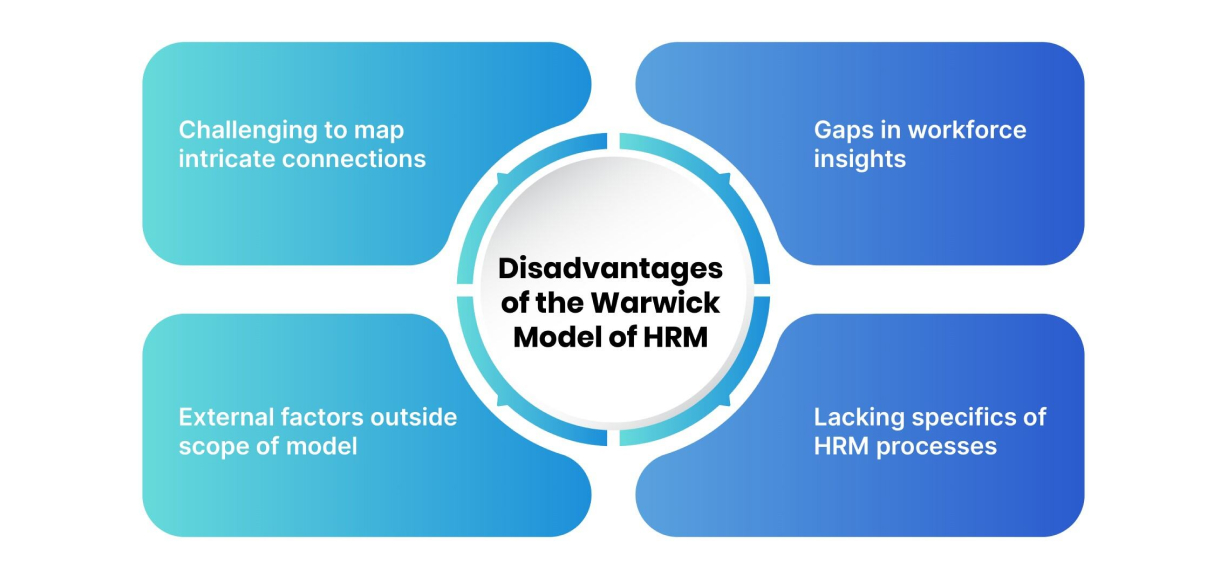
While a key strength of the Warwick Model is that it recognizes the impact of both macro-environmental forces and micro-environmental factors on HRM, mapping out the intricate connections between these forces can be complicated in practice. There are many moving parts to consider, from wider socio-economic trends to internal company politics. Trying to analyze and respond to all of these variables can be an overwhelming task.
The conceptual levers that the model provides do not always easily translate into concrete HRM strategies and interventions. Despite the model's attempt to simplify these dynamics, there is still potential for misalignment or practical disconnection between context and HRM content.
Additionally, the Warwick Model focuses specifically on contextual categories like political-legal forces, structure, culture etc. However, in today's highly interconnected world, there are many other external dynamics that can impact organizations and their HRM function. Things like social media, unexpected socio-political events, global supply chain shocks or emerging tech disruptions may not fit neatly into the model's categories.
So while the Warwick Model encourages HRM to be responsive to the broader environment, it has some inherent limitations in its ability to account for parallel external forces outside its predefined contextual scope.
The Warwick Model places a lot of emphasis on business strategy alignment and the broader organizational ecosystem impacting HRM. However, there could be some gaps in insights relating specifically to the workforce itself. For instance, the model does not provide an inherent framework for delving into the psychology, motivations, and specific capabilities of employees.
Factors like engagement drivers, learning styles, workforce demographics etc. that provide richness in understanding the workforce may not get highlighted explicitly when taking a strategy-focused view. So there is a possibility that intricacies around the people/talent side of the system get underrepresented.
While the Warwick Model provides a broad structural overview of the context, strategy and high-level HRM content domains, it does not get down to the specifics of actual HRM processes. There are no direct insights mapping the contribution of tactical activities like performance management cycles, L&D interventions, recruitment methods etc. towards the overall coherent HRM system that the model advocates.
There is little clarity on how routine HR functional practices fundamentally enable or execute higher order strategic HRM intentions. So the model remains conceptual without illuminating tactical mechanisms.
The Warwick Model offers a structured approach for HR leaders to assess all factors affecting human resource management. It allows organizations to frame integrated policies keeping in mind the business priorities as well as ground realities. Using the model, HR can become a mission-critical function through evidence-based talent decisions.
While the model has some limitations in terms of practical applications, as an overarching strategic framework it adds immense value in shaping the evolution of HR in tandem with dynamic business landscapes.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.